A case for wireless broadband, part 2 (Read part 1 here)
When the wired and wireless alternatives have similar performance and reliability, wireless generally wins due to convenience and cost. This is exactly what is happening at the edge of the network. Wireless technologies are advancing faster than most people realize. When people think of wireless, they think of mobile or Wi-Fi as a complement to wired networks.
Atul Bhatnagar – CEO, Cambium Networks
In our modern, interconnected world, wireless communication has become an integral part of our daily lives. With the ever-growing demand for faster, more reliable, and efficient data transmission, technological innovations have been instrumental in meeting these requirements.
One such innovation is Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access, or OFDMA, the defining principle of the 802.11ax wireless standard.
In this article, we shall delve into the core principles of OFDMA, its applications, and its impact on the world of wireless broadband.
Demystifying OFDMA: What is it and how does it work?
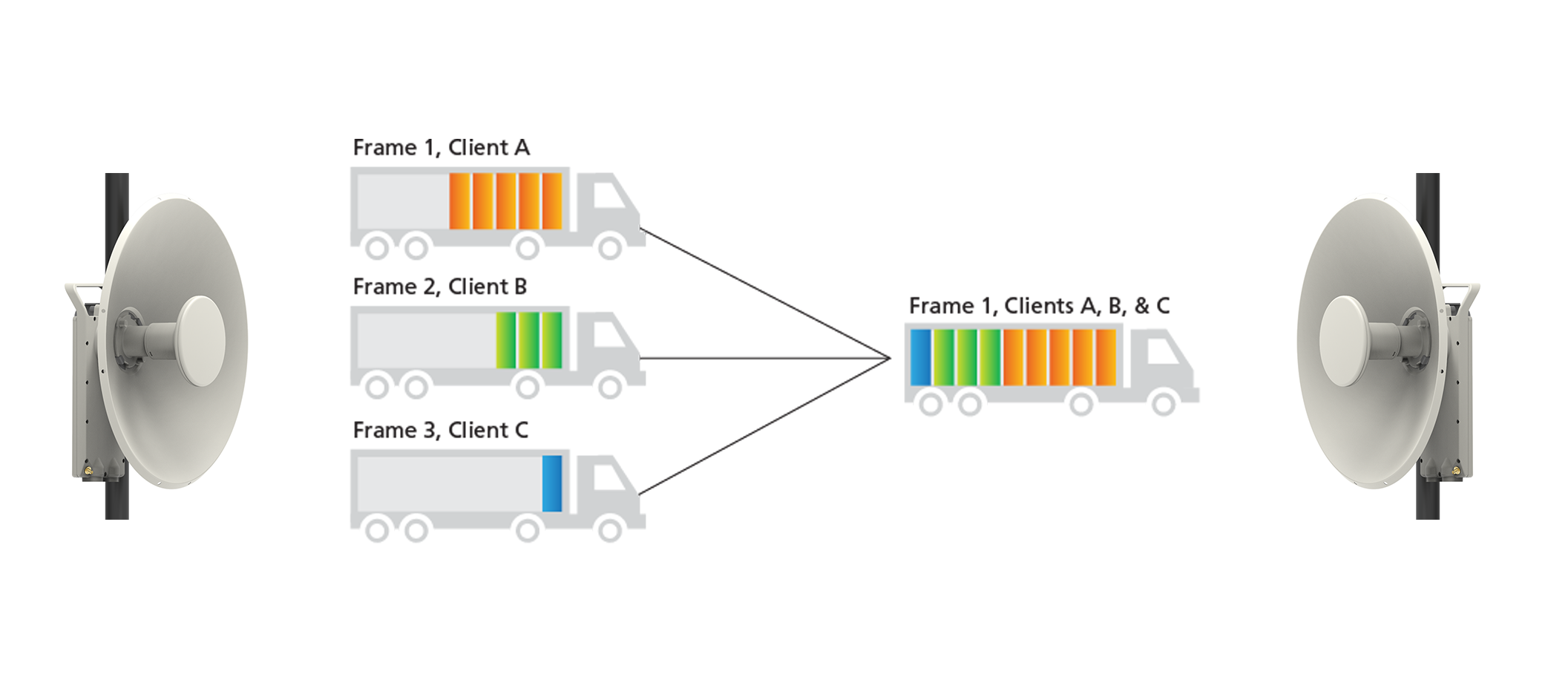
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) is a modulation technique and a multiple-access scheme that enhances the efficiency and reliability of wireless communication. OFDMA builds upon the principles of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), which divides a high-rate data stream into multiple subcarriers, each carrying a portion of the data.
Even though OFDM helps receivers efficiently separate each signal, there is still a lingering limitation in that wireless access points can only process one user's data transmission at a time for each channel. Basically, if multiple users are on one channel, each one has to wait its turn. OFDMA takes this a step further by adding a layer of multiple access, allowing multiple users to access these subcarriers simultaneously.
Using a banking hall analogy, think of the frustration you feel when there are several people in front of you and you know waiting for them to be served is going to slow you down. OFDMA is like the introduction of mobile banking, allowing the bank (your wireless access points) to strategically handle multiple orders simultaneously and better satisfy customers. It's a way of quickly scheduling multiple transactions at once and making sure that everyone gets served in a timely fashion.
Key Principles of OFDMA
1. Orthogonality: The term "orthogonal" in OFDMA refers to the subcarriers being orthogonal to each other. This means that the subcarriers do not interfere with each other, allowing multiple users to access different subcarriers without causing mutual interference. Learn more about orthogonality here.
2. Flexibility: OFDMA provides a high degree of flexibility by allocating different numbers of subcarriers to different users based on their data rate requirements. Users with higher bandwidth needs are allocated more subcarriers, while those with lower bandwidth needs are given fewer subcarriers.
3. Efficiency: By allowing multiple users to share the available bandwidth simultaneously, OFDMA significantly improves spectral efficiency. This is particularly crucial in environments with high user density or varying data rate demands.
Key advantages of OFDMA
- Lower latency: Arguably the biggest advantage of OFDMA routers is their reduced latency, which is especially important in real-time applications such as IoT, online gaming, or audio/video conferencing.
- Higher throughput: By dividing a single channel into multiple subcarriers and assigning them to different users, OFDMA can increase the total maximum throughput of a network.
- Increased network capacity: By allowing multiple users to simultaneously transmit and receive data, OFDMA can increase network capacity, allowing for more devices to connect to a network without compromising performance.
- Improved power efficiency: OFDMA can help reduce power consumption on client-side equipment by enabling them to transmit and receive data more efficiently, leading to lower electric bills or longer battery life.
- Backward compatibility: When you enable OFDMA on an access point, you don't prevent WiFi 5 (802.11ac) or older devices from connecting to your network.
Industry applications of OFDMA
OFDMA technology has found applications in a wide range of industries and use cases, where efficiency and reliability in terms of low latency and high throughput are paramount. Some notable applications include
- Wireless Cellular Networks: OFDMA is a fundamental technology in 4G and 5G networks. It enables multiple users to share the available bandwidth efficiently, resulting in faster data rates, better network capacity, and improved coverage.
- Wi-Fi: The latest Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6, rely on OFDMA to enhance network performance, especially in crowded areas where numerous devices compete for access.
- Satellite Communication: OFDMA technology is employed in satellite communication to improve the efficiency and reliability of data transmission, ensuring high-quality television broadcasts, internet access, and data exchange in remote areas.
- Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint Communication: In applications like fixed wireless broadband, OFDMA is used for point-to-point and point-to-multipoint communication, enabling spectral efficiency, low latencies and higher throughput.
In Summary
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) is a groundbreaking technology that has had a profound impact on wireless broadband.
Its key principles of orthogonality, flexibility, and efficiency have made it a pivotal component in various industries, from cellular networks and Wi-Fi to satellite communication and broadband access.
As the demand for faster, more reliable wireless broadband continues to grow, OFDMA stands as a critical innovation, helping eliminate performance bottlenecks by unlocking the potential for more efficient and robust data transmission and ultimately shaping our increasingly connected world. This makes wireless equipment that feature OFDMA worth the extra cost for all users who seek to achieve the best online experience possible.
Latest Articles
Wed Mar 04 2026
In Education, Cheap Networks are Often the Most ExpensiveFri Feb 13 2026
Why Outdoor Connectivity is Still a Headache for Many HotelsThu Feb 12 2026
Why “Works in the Lab” Often Fails in Production Networks.Related Articles
.jpg)
ePMP 3000 - 5X Performance with Gen3 Technology
-(1).png)
Africa Tech Festival Displays Strides in Connectivity and Telecommunications Infrastructure across Africa

Cambium Networks ePMP Force 425 - The Industry’s First Point-to-Point Solution Based on 802.11ax

If It Can Be Wireless, It Will Be Wireless

© 2026 PoweredbyOptace Networks Limited. All Rights Reserved.
